Apps for individuals diagnosed with breast cancer: a preliminary assessment of the content and quality of commercially available apps in Spanish
Introduction
Breast cancer is the second most frequent tumor in the world and, by far, the most prevalent type of cancer among women, regardless of the level of development of the country in which they live (1). There is sufficient evidence to suggest that there are factors whose elimination may help women prevent the onset of breast cancer (2-5), as well as other factors whose presence, once the tumor is diagnosed, may improve the quality of life and chance of survival of the affected woman (6,7).
Taking action to reduce or remove risk factors and enhance protective factors may reduce the likelihood of suffering from a breast tumor (8) and improve the course of the tumor once it has been diagnosed (9). Multiple strategies and resources have been used over time. However, the use of mobile tools, popularly known as apps, has recently been incorporated.
The contents of many apps are directly related to health issues, such as physical activity (10), assistance in making health-related decisions (11), and weight management (12). Previous studies have shown that this type of tool has long been accepted by the population (13), which has led some authors to suggest that they should be incorporated into health services (10). At the same time, the use of health apps is of interest due to the paradigm shift we are witnessing in healthcare towards patient empowerment or a patient-centered model of health care (14). There is no doubt that this is a real option. Nonetheless, for it to be truly fruitful, the apps recommended by the health services should meet minimum quality standards, such as, for example, proven empirical effectiveness (15,16).
It may be safe to conclude that apps bring benefits in the context of health. However, when used expressly for health issues, existing apps must be reviewed and their contents, aims, and quality determined (17,18). This would allow health care professionals to recommend them to patients. At present, specifically in oncology, the prescription of apps is not popular, one of the reasons being the lack of help provided to clinicians in determining which app is the most appropriate for each patient (18).
In Spain, no study has been found to determine which apps are aimed at addressing any aspect of breast cancer. The objective of this study was to identify and describe the contents and analyze the quality and behavior change strategies of the free applications available in the online stores of Android and Apple whose main purpose is related to some aspect of breast cancer.
Methods
Search strategy and data extraction
Our methods sought to replicate the way a patient might access an app that includes breast cancer information. Searches were conducted in the Apple App and Google Play stores in Spain, between October 2018 and February 2019, using an Apple iPad Pro and a Samsung Galaxy Tab A6. The Spanish search terms used on both online stores were the following: “cáncer de mama” [breast cancer], “cáncer de pecho” [breast cancer], “cáncer de seno” [breast cancer], “tumor de mama” [breast tumor], “tumor de pecho” [breast tumor], “tumor de seno” [breast tumor], “neoplasia de mama” [breast neoplasm], “neoplasia de pecho” [breast neoplasm], and “neoplasia de seno” [breast neoplasm].
The free apps available on both stores were included in this review. The initial screening consisted of reading the description of the apps and downloading them for further evaluation. Two researchers (LlF, RM) used the apps and extracted data from their contents independently. The inclusion criteria were as follows: applications that (I) focused specifically on the prevention or treatment of breast cancer; (II) were free to download and use; and (III) were available in Spanish from Spain. The exclusion criteria were the following: (I) apps that required a wearable device to be used; and (II) apps that did not work or were malfunctioning.
Both researchers (LlF, RM) screened the selected applications independently and extracted their data into a study-specific coding form. The extracted data included: name of the application; available on Apple, Android, or both; and content description. After screening, the researchers downloaded and used the apps. The included apps were installed on the devices for 2 weeks. Contents related to breast cancer, quality (19), and behavioral change (20) were assessed. Throughout this process, any disagreements regarding inclusion or content assessment were resolved by discussion and/or consultation with a third researcher (MA).
App quality assessment
The objective and subjective quality of each app was assessed by consensus between two researchers (LlF, CL) using the Spanish version of the Mobile App Rating Scale (MARS), developed by Stoyanov et al. (21), whose Spanish version was validated by Martin Payo et al. (19). MARS includes 23 items rated on a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (“poor”) to 5 (“excellent”), except items 14–17 and item 19, which also included the “not applicable” option. The 19 items covering objective quality were divided into 4 subscales: engagement (items 1 to 5), functionality (items 6 to 9), aesthetics (items 10 to 12), and information (items 13 to 19). From the scores for individual items were obtained mean quality scores for each subscale. The objective quality total score was calculated as the mean of the scores for the 4 subscales. A mean subjective quality score was obtained as the mean of the scores for items 20–23. Finally, a 6-item app-specific content classification from MARS (awareness, knowledge, attitudes, intention to change, help seeking, and behavior change), designed for use in a health context, was included, in which responses were ratings between 1 (“strongly disagree”) and 5 (“strongly agree”).
Behavioral change content assessment
The behavioral change techniques (BCTs) included in the apps were assessed using the Behavioral Change Techniques Taxonomy version 1, developed by Michie et al. (20). This taxonomy includes 93 BCTs and has been shown to be a valid approach for assessing both BCTs in general, as well as health apps. A dichotomous scoring system was applied, as in previous studies (17), to assess the absence (0) or presence (1) of each BCT. This taxonomy generates a total BCT score per app (range 0–93).
Statistical analysis
A qualitative content analysis was conducted to determine the theme included in the apps. The total scores for each app on each MARS domain and BCT taxonomy were calculated using descriptive analyses. To analyze the differences in quality scores between the apps, the ANOVA test was used. All statistical analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS version 24.0, with the statistical significance threshold set at P<0.05.
Results
App selection and description
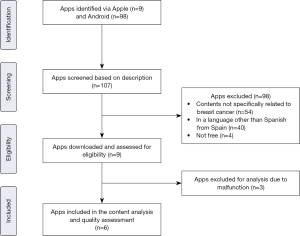
A total of 107 apps were identified and screened. Of those, 98 were excluded. Nine apps were downloaded, used, and assessed for eligibility. Finally, 6 apps, coded as APP1 to APP6, were included (Apple =2, Android =5, both =1). The reasons for exclusion after screening were the following: app contents not specifically related to breast cancer (n=54); in a language other than Spanish from Spain (n=40); and not being free (n=4) (Figure 1).
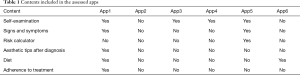
The contents of the 6 selected apps were related to 6 major themes, notably breast self-examination and information related to signs and symptoms that may warn the woman of the presence of a breast tumor (Table 1).
Full table
Quality analysis of the apps
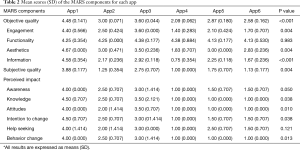
The MARS objective and subjective quality scores were 3.06 (SD =0.802) and 1.96 (SD =1.132), respectively. Disparate scores were observed for both objective quality and subjective quality. Significant differences were observed between the apps and AAP 1 stands out as the best rated, both in terms of objective and subjective quality and in the six items specifically designed for use in a health context (Table 2).
Full table
Behavioral change techniques included in the apps
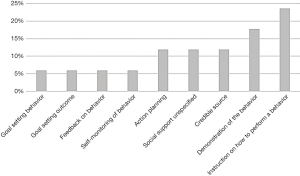
Overall, the mean number of BCTs included in the apps was 2.83 (SD =3.040). The app with the highest number of BCTs was APP1, with a total of 9 techniques. Figure 2 shows the BCTs and their frequency of appearance in the apps. The presence of “Instruction on how to perform a behavior” stands out from the rest of BCTs.
Discussion
The results of the present study highlight the existing apps, designed in Spanish from Spain, whose final objectives are directly related to the prevention of breast cancer and other aspects of special relevance after a breast cancer diagnosis, such as, for example, the therapeutic regimen.
It should be noted that, unlike other assessments of breast cancer-related apps found in the literature, the number of apps is lower, although the selected apps coincide in terms of content (22).
The presence of information relating to self-examination is particularly noteworthy. Four of the six assessed apps included information about the proper procedure for performing this technique. Even though there is controversy in the literature about the usefulness of this technique (23), this method is still the most widely used by women in some contexts (24), which suggests that the breast self-examination technique should not be completely discarded (25) and perhaps women should be trained to do it properly, especially in the absence of other resources (26).
Thanks to the scientific advances in recent years, the prognosis of breast cancer has improved. Screening and early detection strategies for some age groups have contributed significantly to this progress (27). In addition, given the influence that some behaviors have on the development of breast cancer, there seems to be consensus on the importance of making women aware of these risk factors, which makes it possible for them to establish preventive measures themselves (28,29). Of the apps assessed, only two included information regarding risk factors, which, as indicated, play a prominent role in the onset of breast cancer and, therefore, more efforts should be made in its dissemination.
Currently, there are algorithms which have been designed to estimate the likelihood of developing breast cancer. Their use makes it possible to determine which risk reduction options are the most effective in the prevention of breast cancer risk (29,30). Although these algorithms have been shown to be valid for population estimates, they appear to be limited when it comes to individualized estimates. Moreover, they include parameters limiting their usefulness, such as the minimum age for estimates (31). However, some authors point out the need to continue carrying out studies to develop more specific tools (32), since they allow women to become aware of their situation and recognize the need to act to reduce potential risks, for example, by adopting healthy lifestyles that may remove modifiable risk factors (30).
In general, the score obtained regarding the quality of the assessed apps indicates that there is clearly room for improvement. Only APP1 obtained high scores in all items. Previous studies have obtained similar data, highlighting the presence of only a small number of highly-rated apps, while most apps could be improved (17). Also have shown that the use of apps brings benefits to people diagnosed with cancer, both physically and psychosocially (33,34). However, in order to achieve these benefits, several authors point to the need for apps to meet minimum quality criteria, such as, for example, scientific endorsement (18) and being accessible to the target population (33,35,36).
In addition, the literature consulted recommends determining which BCTs are included in the apps. BCTs serve as indicators of the effectiveness of educational interventions. Therefore, having a classification of apps according to the BCTs they include would help select the most appropriate apps in terms of effectiveness (20). According to these authors, the use of BCTs helps to better understand the mechanisms that influence behavioral changes in the population. The number of BCTs identified in the assessed apps was lower than those included in apps assessed in previous studies. In recent studies, such as the study carried out by Yang et al. (10), a total of 39 BCTs of the 93 BCTs available were identified, while Martín-Payo et al. (17) found an average of 3.96 BCTs per app. It would therefore appear that BCT content could also be improved. The BCTs most frequently found in the apps did coincide with the BCTs reported in the literature, such as “providing instruction on how to perform a behavior” (37) or “feedback on behavior” (17).
Limitations of this study include the inclusion of only free apps and apps designed in Spanish from Spain. Both restrictions were made deliberately, as they conform to Spain’s free and universal health care model, as well as to avoid potential confusion from semantic differences between the Spanish spoken in Spain and the Spanish spoken in other countries.
In conclusion, on a positive note, it is worth highlighting the availability of apps in Spanish that are specifically related to breast cancer, breast cancer prevention, and other aspects that may undoubtedly help women who have been diagnosed. However, it should also be noted that the contents and quality of these apps, as well as the number of BCTs they include, should be improved so that they can be safely recommended to this population.
Acknowledgments
Funding: None.
Footnote
Provenance and Peer Review: This article was commissioned by the Guest Editor (Mei R Fu) for the series “Real-Time Detection and Management of Chronic Illnesses” published in mHealth. The article was sent for external peer review organized by the Guest Editor and the editorial office.
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/mhealth-19-191). The series “Real-Time Detection and Management of Chronic Illnesses” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Statement: The authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Open Access Statement: This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), which permits the non-commercial replication and distribution of the article with the strict proviso that no changes or edits are made and the original work is properly cited (including links to both the formal publication through the relevant DOI and the license). See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
References
- The Global Cancer Observatory. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/20-Breast-fact-sheet.pdf
- Colditz GA, Peterson LL. Obesity and Cancer: Evidence, Impact, and Future Directions. Clin Chem 2018;64:154-62. [PubMed]
- Emaus MJ, van Gils CH, Bakker MF, et al. Weight change in middle adulthood and breast cancer risk in the EPIC-PANACEA study. Int J Cancer 2014;135:2887-99. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Liu Y, Nguyen N, Colditz GA. Links between alcohol consumption and breast cancer: a look at the evidence. Womens Health (Lond) 2015;11:65-77. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Ma H, Ursin G, Xu X, et al. Reproductive factors and the risk of triple-negative breast cancer in white women and African-American women: a pooled analysis. Breast Cancer Res 2017;19:6. [PubMed]
- Benton MJ, Schlairet MC, Graham HL. Physical activity-related quality of life in breast cancer survivors compared to healthy women. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 2019;28:e13142. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Nageeti TH, Elzahrany HR, Gabra AO, et al. Quality of life assessment of breast cancer patients in Saudi Arabia. J Family Community Med 2019;26:98-102. [PubMed]
- Sun YS, Zhao Z, Yang ZN, et al. Risk Factors and Preventions of Breast Cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2017;13:1387-97. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Fu MR, Axelrod D, Guth AA, et al. mHealth self-care interventions: managing symptoms following breast cancer treatment. Mhealth 2016;2:28. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Yang CH, Maher JP, Conroy DE. Acceptability of mobile health interventions to reduce inactivity-related health risk in central Pennsylvania adults. Prev Med Rep 2015;2:669-72. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Miller DP Jr, Weaver KE, Case LD, et al. Usability of a Novel Mobile Health iPad App by Vulnerable Populations. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2017;5:e43. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Serrano KJ, Yu M, Coa KI, et al. Mining Health App Data to Find More and Less Successful Weight Loss Subgroups. J Med Internet Res 2016;18:e154. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Boulos MN, Wheeler S, Tavares C, et al. How smartphones are changing the face of mobile and participatory healthcare: an overview, with example from eCAALYX. Biomed Eng Online 2011;10:24. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Moug SJ, Bryce A, Mutrie N, et al. Lifestyle interventions are feasible in patients with colorectal cancer with potential short-term health benefits: a systematic review. Int J Colorectal Dis 2017;32:765-75. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Schoeppe S, Alley S, Van Lippevelde W, et al. Efficacy of interventions that use apps to improve diet, physical activity and sedentary behaviour: a systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2016;13:127. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Wang Q, Egelandsdal B, Amdam GV, et al. Diet and Physical Activity Apps: Perceived Effectiveness by App Users. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2016;4:e33. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Martín Payo R, Harris J, Armes J. Prescribing fitness apps for people with cancer: a preliminary assessment of content and quality of commercially available apps. J Cancer Surviv 2019;13:397-405. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Pandey A, Hasan S, Dubey D, et al. Smartphone apps as a source of cancer information: changing trends in health information-seeking behavior. J Cancer Educ 2013;28:138-42. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Martin Payo R, Fernandez Álvarez MM, Blanco Díaz M, et al. Spanish adaptation and validation of the Mobile Application Rating Scale questionnaire. Int J Med Inform 2019;129:95-9. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Michie S, Wood CE, Johnston M, et al. Behaviour change techniques: the development and evaluation of a taxonomic method for reporting and describing behaviour change interventions (a suite of five studies involving consensus methods, randomised controlled trials and analysis of qualitative data). Health Technol Assess 2015;19:1-188. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Stoyanov SR, Hides L, Kavanagh DJ, et al. Mobile app rating scale: a new tool for assessing the quality of health mobile apps. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2015;3:e27. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Ginossar T, Shah SF, West AJ, et al. Content, Usability, and Utilization of Plain Language in Breast Cancer Mobile Phone Apps: A Systematic Analysis. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2017;5:e20. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Nelson AL. Controversies regarding mammography, breast self-examination, and clinical breast examination. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 2013;40:413-27. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Leon-Rodriguez E, Molina-Calzada C, Rivera-Franco MM, et al. Breast self-exam and patient interval associate with advanced breast cancer and treatment delay in Mexican women. Clin Transl Oncol 2017;19:1276-82. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Sociedad Española de Oncología Médica. Available online: https://seom.org/seomcms/images/stories/recursos/Manual_SEOM_Prevencion_2017.pdf
- Azemfac K, Christie SA, Carvalho MM, et al. A Community-Based Assessment of Knowledge and Practice of Breast Self-Examination and Prevalence of Breast Disease in Southwest Cameroon. J Cancer Epidemiol 2019;2019:2928901. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- DeSantis CE, Bray F, Ferlay J, et al. International Variation in Female Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2015;24:1495-506. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Sauter ER. Breast Cancer Prevention: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Eur J Breast Health 2018;14:64-71. [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy A, Soundara V, Ramshankar V. Preventive and Risk Reduction Strategies for Women at High Risk of Developing Breast Cancer: a Review. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2016;17:895-904. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Costa M, Saldanha P. Risk Reduction Strategies in Breast Cancer Prevention. Eur J Breast Health 2017;13:103-12. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Wang X, Huang Y, Li L, et al. Assessment of performance of the Gail model for predicting breast cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Breast Cancer Res 2018;20:18. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Advani P, Moreno-Aspitia A. Current strategies for the prevention of breast cancer. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press) 2014;6:59-71. [PubMed]
- Phillips SM, Conroy DE, Keadle SK, et al. Breast cancer survivors' preferences for technology-supported exercise interventions. Support Care Cancer 2017;25:3243-52. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Puszkiewicz P, Roberts AL, Smith L, et al. Assessment of Cancer Survivors' Experiences of Using a Publicly Available Physical Activity Mobile Application. JMIR Cancer 2016;2:e7. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Coughlin SS, Thind H, Liu B, et al. Towards research-tested smartphone applications for preventing breast cancer. Mhealth 2016;2:26. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Hong YA, Goldberg D, Ory MG, et al. Efficacy of a Mobile-Enabled Web App (iCanFit) in Promoting Physical Activity Among Older Cancer Survivors: A Pilot Study. JMIR Cancer 2015;1:e7. [PubMed]
- Conroy DE, Yang CH, Maher JP. Behavior change techniques in top-ranked mobile apps for physical activity. Am J Prev Med 2014;46:649-52. [Crossref] [PubMed]
Cite this article as: Martín-Payo R, Ferreras-Losilla L, González-Méndez X, Leirós-Díaz C, Martínez-Urquijo A, Fernández-Álvarez MDM. Apps for individuals diagnosed with breast cancer: a preliminary assessment of the content and quality of commercially available apps in Spanish. mHealth 2021;7:2.